Refusal of Property Registration
Refusal of Property Registration
Util Menu
Refusal of property registration
Eligibility for refusal of property registration
If a civil servant’s lineal ascendant or descendant is not a dependent of the civil servant, the person may refuse to report and register property with approval from the Civil Service Ethics Committee
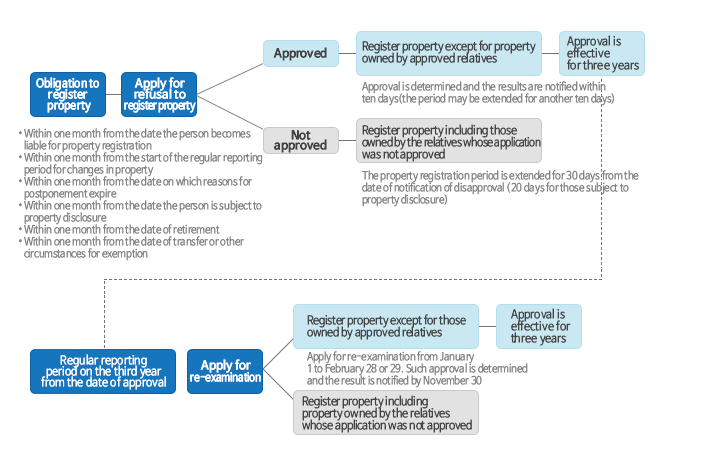
Application for refusal of property registration
- (For approval) An application shall be submitted by January 31 in the case of regular reporting or within 1 month from the date of registration/reporting in the case of non-regular reporting
* employment, promotion, exemption, end of postponement, re-registration, or retirement - (For re-examination) Request for re-examination shall be submitted during the regular reporting period on the third year following the approval (January 1 to February 28)
Process of Application for Refusal
Documents to be submitted
An application form for refusal of property registration (Form 14 of the Enforcement Rule on the Civil Service Ethics Act) and a supporting document on independence
Conditions for approval
The applicant shall not be a dependent (Article 27-2, Paragraph 1 of the Enforcement Decree on the Civil Service Ethics Act)
A dependent refers to a lineal ascendant or descendant who is unable to earn his or her living independently due to the lack of or an inadequate income and is thus financially supported by a civil servant subject to property registration.
The applicant shall earn his or her living independently (Article 27-2, Paragraph 2 of the Enforcement Decree on the Civil Service Ethics Act)
- Lineal ascendants: age, employment status, property owned, and regular income from work, business or property are comprehensively considered
- Lineal descendants: age, formation of a separate household, employment status, employment period, and regular income from work or business are comprehensively considered