Blind Stock Trusts
Blind Stock Trusts
Util Menu
Purpose of blind stock trusts
To prevent conflicts of public and private interests in the performance of government duties that may arise from ownership of stocks relevant to a civil servant’s job
Subjects and criteria
Stocks exceeding KRW 30 million in aggregate owned by civil servants subject to property disclosure, or civil servants of Grade 4 or above at finance bureaus of the Ministry of Economy and Finance or the Financial Services Commission, and their interested parties (spouses, lineal ascendants and descendants)
Key features
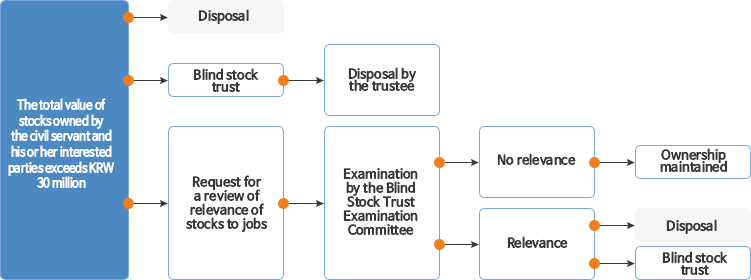
- In principle, relevant stocks shall be disposed of or be placed in a blind stock trust
- If a civil servant wishes to obtain exemption, the person shall make a request for a review of the relevance of the stocks to his or her job to the Blind Stock Trust Examination Committee and receive the Committee’s ruling that the stocks have no relevance to their work duties
Determination of stock price
- Listed stocks: final traded price on the date of the property report
- Over-the-counter (OTC) stocks traded similar to those on an exchange: base price on the date of property report (volume-weighted average price)
* Article 166 of the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act
* Price of stocks traded on the K-OTC market is determined based on their volume-weighted average price
- Other unlisted stocks
* Price of unlisted stocks traded on the K-OTC market is determined based on their volume-weighted average price
- ①Stocks are traded on the market and meet the conditions for use of actual transaction price → Use actual transaction price
If actual transaction price is below face value → Use face value
- Stocks have been traded during the period of 6 months from the property registration date ② with a third party who is not a civil servant subject to property registration or an interested party ③ for amounts exceeding 1% of the total number of shares issued or KRW 300 million (face value) ④ with tax reports in existence, such as tax reports on capital gains, that prove actual transactions
- ②Stocks are not traded on the market or do not meet the conditions for use of actual transaction price → Use valuation price
Calculation of valuation price
- 1. The higher of the following becomes the stocks’ valuation price
- a. Net income per share (the weighted average net income of the last 3 years per share ÷ interest rate prescribed by the enforcement decree) × 3/5 + net asset per share (net asset ÷ total no. of shares in issue) × 2/5
- b. Net asset per share × 4/5
- c. Face value per share
- 2. Notwithstanding the above, if the stocks meet any of the following conditions, the net asset per share becomes the stocks’ valuation price
- a. Stocks of a company with a business continuity issue due to on-going liquidation, the death of the owner, etc. during the property registration or property change reporting period
- b. Stocks of a company whose business has not officially commenced operation, has been in operation less than 4 years, or is in business suspension or discontinuation
- 1. The higher of the following becomes the stocks’ valuation price
Conditions that trigger the blind stock trust obligation
- The amount of stocks owned exceeds KRW 30 million (including when the market value increases to exceed KRW 30 million)
- The civil servant becomes subject to property disclosure
- Reasons for postponement of reporting changes expire (Article 6-3, Paragraph 1 and 2 of the Civil Service Ethics Act)
- The civil servant is notified that the stocks have relevance to his or her job
- The civil servant makes a blind stock trust arrangement and thereafter his or her interested party acquires stocks as a promoter of the stock issuing company (proviso in Article 14-6, Paragraph 1 of the Civil Service Ethics Act)
- The civil servant makes a blind stock trust arrangement and thereafter acquires new stocks through inheritance or gifts (Article 27-9 of the Enforcement Decree on the Civil Service Ethics Act)
- Changes are made to the civil servant’s job (e.g. standing committee, assignment)
※ For instance, changes are made to the standing and special committees of members of the National Assembly and local council, director of OO local police agency is assigned to the director of △△ local police agency, the deputy minister at □□ office is assigned to △△ office of the same bureau, or changes are made to the deputy minister’s ○○ office as a result of restructuring (e.g. new duties)
Process of blind stock trusts